Updated: 20 May, 2025
17 June, 2022
In the era of data-driven innovation, software development plays a critical role in managing sensitive personal information. However, the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has introduced complex challenges for software developers seeking to ensure their products comply with this far-reaching regulation. At Codific, we bring over a decade of experience crafting secure software that aligns with GDPR standards across diverse industries, including Ed-Tech, HR-tech, and AppSec. Our deep understanding of data privacy and security has positioned us at the forefront of compliance with evolving regulations. To help you navigate the intricacies of GDPR compliance in software development, we’ll share our expertise in this comprehensive guide.
Key takeaways
- The GDPR is a complex regulation that imposes stringent requirements on organizations worldwide.
- To develop GDPR-compliant software, it’s crucial to understand the regulation’s fundamental terms.
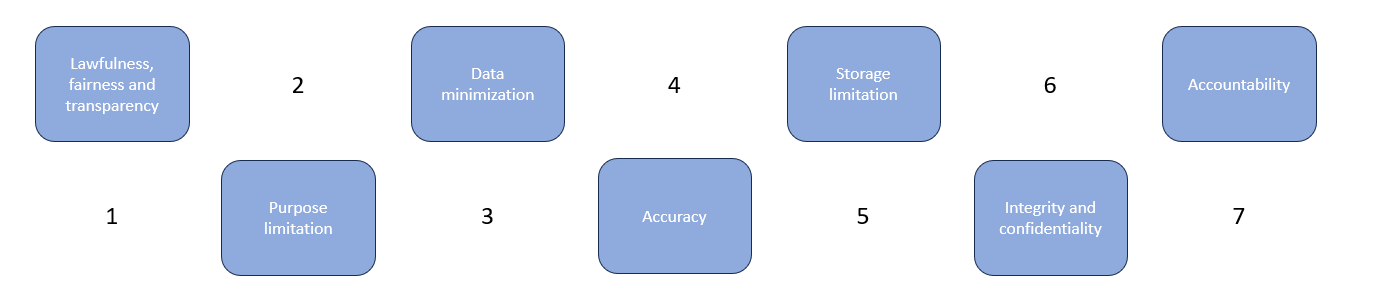
- The GDPR’s 7 data protection principles are the foundation of compliance. These are:
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency.
- Purpose limitation.
- Data minimization.
- Accuracy.
- Storage limitation.
- Integrity and confidentiality.
- Accountability.
- Codific specializes in building secure software that meets GDPR standards.
- Codific’s Attendance Radar app exemplifies GDPR compliance principles.
Delving into the GDPR and its key definitions
The GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation, the EU’s landmark data privacy and security law that imposes stringent requirements on organizations worldwide. It applies to any organization that targets or collects data related to individuals residing in the EU, regardless of their location. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, making achieving GDPR compliance a crucial endeavor.
For GDPR compliance in software development, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental legal terms defined within the regulation:
- Personal Data: We consider any information that links to an identifiable individual as personal data, including names, email addresses, ethnicity, gender, biometric data, and other sensitive information. We classify pseudonymized data under this definition if it can be linked to an individual with reasonable effort.
- Data Processing: Any operation performed on personal data, whether automated or manual. This encompasses collection, storage, retrieval, use, disclosure, erasure, or destruction of personal data.
- Data Subject: The individual whose personal data is being processed.
- Data Controller: The organization or individual responsible for deciding why and how personal data will be processed.
- Data Processor: A third-party organization that processes personal data on behalf of the data controller.
To achieve GDPR compliance, it’s essential to integrate the regulation’s data protection principles into your software development workflow. These principles, including lawfulness, fairness and transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality, and accountability, are the foundation of GDPR compliance. In the next section, we’ll explain these principles and explore how to incorporate them in your development process.
7 Key Principles for GDPR Compliance in Software Development
To achieve GDPR compliance, it’s essential to integrate the regulation’s data protection principles into your software development workflow. These principles, including lawfulness, fairness and transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality, and accountability, are the foundation of GDPR compliance. In the next section, we’ll explain these principles and explore how to incorporate them in your development process.
1. Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Organizations must always conduct data processing lawfully, fairly, and transparently. They must inform data subjects about the collection, use, and storage of their personal data and grant them the right to access, rectify, and erase their data.
2. Purpose limitation
Personal data should only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Additional and future processing of data should still follow these initial purposes.
3. Data Minimization
Only the minimum amount of personal data necessary for the specified purposes should be collected. This means avoiding collecting excessive or irrelevant data.
4. Accuracy
Personal data should be accurate and kept up to date. Organizations should take reasonable steps to rectify any inaccurate data promptly.
5. Storage Limitation
Organizations should keep personal data for no longer than is necessary for the specified purposes. They should implement appropriate measures to dispose of or anonymize personal data when it is no longer needed.
6. Integrity and Confidentiality
We should process personal data in a manner that ensures appropriate security, including protecting it against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction, or damage. Organizations should implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect data security.
7. Accountability
The data controller must be able to demonstrate compliance with the GDPR. This includes keeping records of data processing activities and being able to respond to data subject requests and data breaches.
By incorporating these seven principles into your software development process, you can effectively protect the personal data of your users and meet the requirements of the GDPR.
GDPR Compliance Checklist for Software Development
1. Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
- Inform users about how their data is collected, used, and stored by implementing clear and accessible privacy notices.
- Obtain explicit consent from users before collecting their personal data.
- Provide options for users to control how their data is used.
- Implement clear and transparent data retention policies.
2. Purpose Limitation
- Identify the specific and legitimate purposes for collecting personal data.
- Collect only the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve the specified purposes.
- Restrict the use of personal data to the purposes for which it was collected.
3. Data Minimization
- Conduct a privacy impact assessment to identify and minimize the collection of personal data.
- Implement data minimization principles throughout the software development lifecycle. Collect only the data strictly necessary for the intended purposes.
- Regularly review and reassess the need to collect personal data. Avoid retaining irrelevant or excessive information for prolonged periods.
4. Accuracy
- Implement data validation and data quality checks to ensure data accuracy through the use of algorithms.
- Provide mechanisms for users to correct or update their personal data.
- Regularly review and update personal data to ensure accuracy.
5. Storage Limitation
- Establish clear data retention policies that specify the retention period for different categories of personal data.
- Implement automated data scrubbing or deletion mechanisms to remove outdated or no longer needed data.
- Provide options for users to request data deletion or anonymization. Ensure backups comply with storage limitations and are securely deleted when no longer needed.
6. Integrity and Confidentiality
- Implement data encryption and access controls to protect personal data from unauthorized access.
- Regularly update security software and patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to identify and remediate security weaknesses.
- Analyzing and working towards improving the application security of your software using renowned AppSec models like SAMM and a management tool like SAMMY to manage the process.
7. Accountability
- Document data processing activities, including the purposes, categories of data, data recipients, and retention periods.
- Implement incident response procedures to identify, contain, and remediate data breaches.
- Conduct regular compliance assessments to ensure ongoing adherence to GDPR requirements.
How do we apply the 7 principles in our applications?
To further illustrate how you can apply the 7 principles in your own software development process, let me briefly explain how we did it in one of our Ed-Tech solutions, Attendance Radar, which is a mobile student attendance tracking app.
a mobile student attendance tracking app.
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency: We apply this principle in Attendance Radar by asking for the consent of data subjects to process their data. When the users first download and register an account in the app, we ask for them to agree to our Terms and Conditions. In this Terms and Conditions, we outline our privacy policy, which explains the data we collect, how we collect it, and how we use and store it.
- Purpose limitation and data minimization: We apply these two principles simultaneously. That is because we only collect the minimal amount of data necessary for the purpose of student attendance tracking. Moreover, we inform users about the purpose of our data collection and explain in our privacy policy why this data is necessary.
- Accuracy: We allow users to modify some of their personal information like their name, surname and student numbers. Additionally, we implement data validation and quality checks for accuracy assurance.
- Storage limitation: Data is stored until it is deleted by a user. Trainers can delete data on their courses and sessions, including the student enrollments onto these courses. Additionally, both trainers and students can at any point delete their account. We keep data for 30 days upon deletion and then anonymize it.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: We use data encryption and access controls to protect data from unauthorized access. Additionally, we conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to identify and patch security vulnerabilities.
- Accountability: Attendance Radar documents its data processing activities and sets up incident response procedures.
What other software do we build with GDPR in mind?
Top universities, academies, and hospitals use Videolab to put the care in healthcare. These institutions train communication skills, empathy, and other soft skills by sharing patient interview recordings for feedback.
SARA is used by top HR-Consultants to deliver team assessments, psychometric tests, 360 degree feedback, cultural analysis and other analytical HR tools.
SAMMY is a Software Assurance Maturity Model management tool. It enables companies to formulate and implement a security assurance program tuned to the risks they are facing. That way other companies can help us build a simple and safe digital future. Obviously our AppSec program and SAMMY itself is built on top of it.
We believe in collaboration and open innovation, we would love to hear about your projects and see how we can contribute in developing secure software and privacy by design architecture. Contact us.