Updated: 30 September, 2025
16 December, 2024
Implementing ISO 27001 is crucial for organisations looking to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with global security standards. This blog will walk you through what ISO 27001 is, how to obtain the certification, and a free tool to implement the ISO 27001 framework.
Listen to the summary of this article on The AppSec Management Podcast:
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an international standard that defines the requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS).

Its purpose is to help organisations of all sizes and activities, establish, implement, monitor, review, maintain, and continually improve their information security practices. The framework focuses on managing risks to information security, which can include data breaches, threats, cyber attacks and more. The process involves a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring it remains secure and confidential, and includes people, processes, and IT systems under a comprehensive risk management framework.
The ISO 27001 certification standard is recognised worldwide as proof that your organisation’s information security management is aligned with best practice.
The ISO 27001 is important as it demonstrates a company’s commitment to protecting sensitive information and managing information security risks effectively. Achieving this certification boosts trust and confidence with your customers or other organisations and stakeholders, and shows your commitment to continuous improvement.
Who is ISO?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is an independent, non-governmental organisation that develops and publishes international standards. Based in Switzerland, ISO brings together experts from 172 national standards bodies to create consensus-based, market relevant standards that support innovation and provide solutions to global challenges.
The ISO vision statement “Making lives easier, safer and better”.
While their mission is “Through our members and their stakeholders, we bring people together to agree on International Standards that respond to global challenges. ISO standards support global trade, drive inclusive and equitable economic growth, advance innovation and promote health and safety to achieve a sustainable future.”
The most popular ISO standards are the following:
- ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems: Focuses on improving quality and meeting customer expectations.
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Information Security Management Systems: Helps organisations protect sensitive information and manage risks.
- ISO 14001 – Environmental Management Systems: Guides organisations in improving their environmental impact.
- ISO 45001 – Occupational Health and Safety: Promotes safe and healthy workplaces by reducing workplace risks.
- ISO 50001 – Energy Management Systems: Helps organisations enhance energy efficiency and reduce consumption.
ISO is highly respected worldwide, with its standards recognized as benchmarks of quality, safety, and efficiency. By implementing ISO standards, organizations demonstrate their commitment to best practices, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement.
Key principles of ISO 27001
The key principles of ISO 27001 are essential to developing and maintaining a robust Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). They focus on ensuring the security and proper management of information within an organisation.
- Confidentiality: this principle ensures that information is accessible only to authorised individuals, preventing unauthorised access, disclosure, or beaches. Organisation achieve this by implementing strong access control, encryption, and secure communication channels to protect sensitive data during storage and transmission.
- Integrity: this guarantees that information remains accurate and unaltered throughout its life cycle. Effective strategies include maintaining up-to-date backups, version control, and monitoring systems to track changes.
- Availability: this ensures authorised users can access information and systems whenever needed, even during disruptions like cyberattacks or natural disasters. Organizations address this by creating disaster recovery plans, redundancies, and robust system designs to minimize downtime and maintain business operations.
These principles are central to risk management within ISO 27001 and serve as the foundation for establishing a secure ISMS that aligns with global best practices. They emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring, updates, and improvements to adapt to evolving threats.

Who should comply with ISO 27001?
Organisations across all industries can implement and comply with ISO 27001 to enhance their information security management practices. While there are no strict limitations on who can adopt the standard, some types of organizations are particularly suited to benefit from ISO 27001 compliance. These organisations can be ones that handle sensitive data such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, government agencies, and cloud service providers. As these organisations manage large volumes of sensitive data, making robust information security systems is essential.
Software developers are also a recommended organisation to comply with this standard. In our case, Codific holds the ISO 27001 certification, which is an indication of some of the many security practices we have in place to protect the company and customers data.
E-commerce, retail, multinational corporations and more, should comply with ISO 27001 to provide a framework for the sensitive information they manage across locations. Companies seeking a competitive advantage will also want to comply, the certification demonstrates a commitment to information security, which is often a prerequisite for certain partnerships or contracts.
Quite often ISO27001 certification is a prerequisite in requests for proposals of larger companies or government institutions. Without the certification suppliers are excluded from bidding for certain contracts.
How to implement ISO 27001
If you’re just getting started, we’ve put together a step guide to help you understand the ISO 27001 requirements in order to obtain the certification. This guide emphasises preparation, practical action, and continual improvement.
Step 1: Secure management support
You need to assign and empower a leader to oversee ISO 27001 implementation. It requires organisational commitment and resources. Without support, securing budgets and enforcing policies become difficult. You will still need a team to support the leader.
Why this matters: Leadership support ensures smooth execution of processes and helps secure necessary budgets.
Key tasks:
- Present the benefits of ISO 27001, such as risk reduction, customer trust, and compliance.
- Have clear objectives and benefits from this process and implementation.
- Understand costs and length of the implementation process.
- Appoint a project sponsor from senior management to oversee progress.
Step 2: Define the ISMS scope
Define what parts of your organisation the ISMS will cover. A clearly defined scope ensures efficient implementation and helps in identifying key stakeholders.
Key tasks:
- Identify organizational units, locations, and processes to include.
- Define stakeholders and regulatory or contractual obligations.
Step 3: Conduct a risk assessment
Perform a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to your information assets.
Why this matters: Risk assessments help prioritise actions and allocate resources effectively.
Key tasks:
- Create an inventory of information assets.
- Analyze threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts.
- Evaluate the likelihood of risks materializing.
Step 4: Develop a risk treatment plan
Based on the risk assessment, decide how to mitigate identified risks. A structured plan ensures risks are addressed systematically.
Key tasks:
- Prioritize risks that require immediate action.
- Ensure staff and other team members that interact with information know their security obligations.
- Apply measures like encryption, access controls, or incident management processes.
- Document your plan for future audits.
Step 5: Establish policies and procedures
Develop comprehensive policies and procedures to ensure consistency and compliance across the organisation. Clear documentation supports training and day to day implementation.
Key tasks:
- Write security policies suited for your organisations, examples are: data protection, incident response, and access controls.
- Ensure these procedures align with ISO 27001 clauses and controls. You can use SAMMY to keep track of all the requirements.
Step 6: Implement the ISMS
Apply the policies, controls, and procedures developed in the previous steps and embed them into daily operations.
Why this matters: Practical application ensures compliance is more than just theoretical.
Key tasks:
- Train employees to follow new procedures.
- Integrate ISMS tasks into business as usual activities.
Step 7: Conduct training and awareness programs
Educate employees about the ISMI, their responsibilities, and best practices for information security.
Why this matters: human errors are a common cause of security breaches, so awareness is critical.
Key tasks:
- Deliver workshops or training sessions.
- Regularly update the team on changes to policies and procedures.
Step 8: Measure, Monitor and audit the ISMS
Regularly review and audit the ISMS to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with ISO 27001.
Why this matters: continuous improvement is a core principle of ISO 27001.
Key tasks:
- Conduct internal audits to identify gaps or weaknesses. You can use SAMMY to run your internal audit and identify the gaps.
- Review the ISMS regularly to adapt to new threats or changes in scope.
Step 9: Prepare for certification
If you aim for certification, work with an accredited certification body to conduct an external audit. Find out more below.
How to Obtain ISO 27001 Certification
Once your ISMS is in place and you wish to obtain the ISO 27001 certification, you have properly prepared for an external audit. The certification process typically involved two stages:
- Stage 1 Audit: This is an initial review of ISMS documentation and readiness. If the auditor is satisfied, they will continue to conduct a more thorough investigation. In this stage 1, it is important that you are confident in your ability to certify, as the second stage is time consuming and very expensive. If you fail, you will be charged either way.
- Stage 2 Evaluation: A detailed evaluation of the ISMS implementation and effectiveness is conducted by the external auditors.
There are many external auditors you can go for, it is important to make sure they are accredited by a national certification body, which should be a member of the IAF (International Accreditation Body).
These global and well-known certification bodies are often preferred for their reputation and expertise:
- BSI Group (British Standards Institution): Offers ISO 27001 certification and extensive training on implementing and managing ISMS.
- TÜV Rheinland: Provides auditing and certification services for various ISO standards, including ISO 27001.
- Lloyd’s Register (LRQA): A global provider of ISO certification with expertise in information security and risk management.
- SGS: Offers ISO 27001 certification services and is recognized for its global reach and industry experience.
- DNV (Det Norske Veritas): Provides ISO 27001 certification and other management system audits with a focus on innovation.
Free tool to help implement ISO 27001
Achieving ISO 27001 certification can be a complex and costly process for many organizations. Especially for those new to security, it can be daunting and may require external consultancy for implementation and maintenance.
To simplify this, organisations can use SAMMY – an AppSec Program Management tool (with a free version). Originally designed for OWASP SAMM, SAMMY now supports multiple security maturity and compliance frameworks, including ISO 27001, BSIMM14, NIST SSDF, NIST CSF 2.0, and more that you can find here. Businesses can use it both as a pre-audit preparation tool and as a continuous management tool after certification.
SAMMY can help you prepare for your ISO 27001 audit by:
- Audit Readiness Check: SAMMY guides organizations through ISO 27001 requirements, ensuring that all mandatory policies, procedures, and controls are in place. It highlights any gaps that need to be addressed before scheduling an external audit.
- Cost Savings: By identifying compliance issues early, SAMMY reduces the risk of audit failures and eliminates the need for expensive pre-audit consulting services.
- Centralized Security Management: The platform provides a unified view of multiple security frameworks, making it easier for organizations to manage their security posture holistically.
- Progress Tracking & Reporting: SAMMY includes tracking features that allow teams to monitor implementation progress and generate compliance reports, simplifying internal audits.
Using SAMMY simplifies the entire ISO 27001 implementation process, helping organisations improve preparation for the audit, reduce costs and boost their chances of passing the certification on the first attempt.
Holding a ISO 27001 does not guarantee security, using a tool like SAMMY gives organisations access to several different security frameworks, exposing and helping your organisations manage and improve your security posture.
Comparison with other compliance frameworks
Comparison of SOC 2 vs ISO 27001
When it comes to managing information security, organizations can face a choice between two leading frameworks: ISO 27001 and SOC 2 (Service and Organisation Controls 2) . Both provide robust approaches to data security, risk management, and compliance. However, they differ in many ways, so let’s take a more detailed look below.
Global Recognition:
- ISO 27001: Internationally recognized and accepted across industries and countries.
- SOC 2: Primarily recognized in North America, especially in the technology and SaaS sectors.
Certification vs Report:
- ISO 27001: Involves formal certification by an accredited certification body after a comprehensive audit. Certification is valid for three years, with annual surveillance audits.
- SOC 2: Results in an attestation report issued by an independent auditor (CPA). There’s no formal “certification,” just a detailed audit report (Type I or Type II).
- SOC 2 Type I evaluates an organization’s IT security controls at a specific point in time. It verifies whether the controls are properly designed but does not assess how well they function over time. This makes Type 1 suitable for companies looking for a quick initial evaluation of their security setup. Can be completed in as little as 45 days if the organization is well-prepared.
- SOC 2 Type II, on the other hand, goes deeper by examining both the design and operational effectiveness of these controls over a set observation period, usually between six months to a year. This type of audit shows whether an organization consistently follows its security processes over time. Typically takes two to six months, depending on organisation processes and preparation. Type II provides greater assurance to clients and stakeholders, as it demonstrates long-term compliance and operational effectiveness.
Applicability:
- ISO 27001: Suitable for organizations of all sizes across industries seeking a structured, risk-based approach to information security management.
- SOC 2: Tailored for service organizations that manage client data, often used by technology and cloud service providers.
Key differences summary:
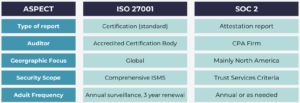
Understanding these differences can help businesses choose the right framework based on their industry, clients, and operational needs.
FedRAMP vs ISO 27001. A comparison
Both FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program) and ISO 27001 are frameworks designed to ensure high levels of data security and compliance.
Global Recognition and Industry Use:
- FedRAMP: Recognized mainly in the U.S. public sector for cloud service providers working with government agencies.
- ISO 27001: Globally recognized and accepted across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and technology.
Security controls:
- FedRAMP: Based on the NIST 800-53 framework, which includes over 300 security controls for managing federal information systems and cloud services.
- ISO 27001: Uses Annex A of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, which includes 114 security controls focused on risk management, data protection, and business continuity.
Requirements:
- FedRAMP is required of any cloud service provider that wishes to work with the US federal government. Outside of the scope of working with the US federal government, FedRAMP is never going to be required
- ISO 27001 is not required at all by any law. However, as the largest and most well-known and well-governed security framework around the world, therefore it is commonly required in contracts and deals.
Certification vs Report:
- FedRAMP: This certification process is designed for cloud service providers to ensure they meet US government security standards. It involves 3 main stages, Security assessment, authorisation, continuous monitoring. The certification is granted by the US government.
- ISO 27001: Requires an independent audit by an accredited certification body. Certification lasts three years with annual surveillance audits.
Key differences summary:
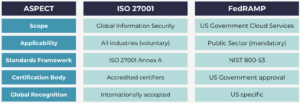
While both frameworks pursue data security, they serve different purposes. The same applies as above, depending on your organisation’s needs, either certification could help demonstrate a strong commitment to data security and risk management. If your organisation operates in the US public sector and also aims to establish global credibility, it is generally recommended for you to pursue both FedRAMP and ISO 27001.
Conclusions
Implementing ISO 27001 is a critical step toward safeguarding sensitive information, enhancing operational resilience, and boosting customer trust. While the journey may seem complex, following a structured approach can help the process.
Leveraging tools like SAMMY allows organisations to streamline security practices. Enabling team collaboration, progress tracking, measure success and automate crucial aspects of AppSec program management.
Achieving ISO 27001 certification should be more than a regulatory checkbox, by adopting best practices and committing to continuous improvement, your organisation can confidently navigate and more towards secure software development.
Ready to take the next step? Start leveraging SAMMY and find the perfect balance between guidance and execution in your AppSec journey.
Official Resources
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022
- ISO 9001
- ISO 14001
- ISO 45001
- ISO 50001
- FedRAMP
- OWASP SAMM
- BSIMM
- NIST SSDF
- NIST CSF 2.0
- NIST 800-53
- SOC 2