Updated: 30 September, 2025
12 December, 2024
HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, is a critical federal law in the U.S. healthcare system. Its designed to improve health insurance portability (ensuring coverage for individuals between jobs and with pre-existing conditions); reduce administrative costs through standardization of electronic healthcare transactions; and protect patient privacy. For effective HIPAA implementation, healthcare organizations establishes national standards for electronic healthcare transactions and protects the privacy and security of patients’ health information by giving patients control over their data and ensuring it is shared securely. These measures help prevent healthcare fraud, improve data security, and increase patient trust in the healthcare system.
How does the HIPAA law protect patient privacy?
HIPAA implementation involves several key mechanisms to protect patient privacy:
- Privacy Rule: This rule sets standards for the use and disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI). It limits how PHI can be used or shared without patient consent. This ensures that only the minimum necessary information is disclosed for treatment, payment, or healthcare operations.
- Patient Rights: Patients have rights to access their health records, request corrections, and receive an account of disclosures. They must be informed about how their information is used through a Notice of Privacy Practices. You can read more on specific patient rights here.
- Safeguards: HIPAA mandates administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for PHI’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These include encryption, access controls, and employee training to prevent unauthorized access.
- Breach Notification Rule: In case of a data breach, covered entities must notify affected individuals and the Department of Health and Human Services promptly.
Steps to Achieve HIPAA Compliance
Achieving HIPAA compliance requires a systematic approach. Organizations must standardize procedures, implement robust security measures and conduct employee training. Moreover, we should note that this is simply the beginning. In order to remain compliant, companies should regularly review and update policies to reflect any changes in HIPAA regulations.
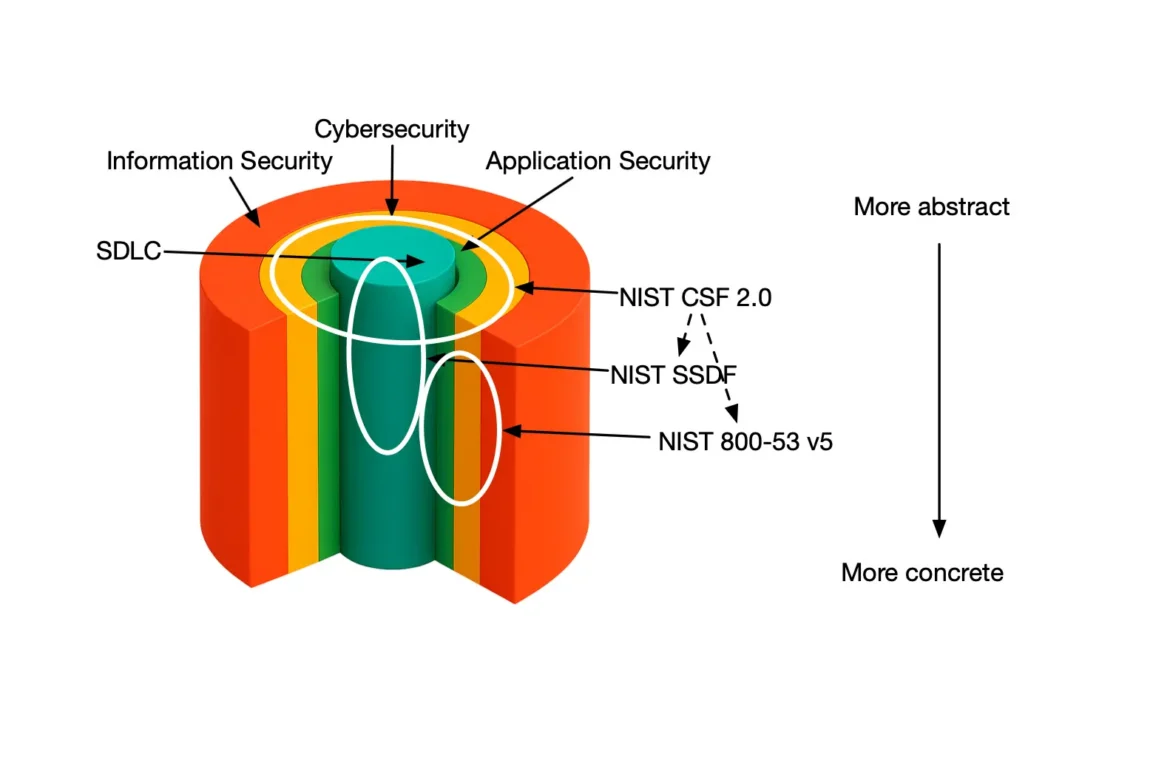
The path to compliance begins with risk assessment, which identifies vulnerabilities in PHI handling systems and helps prioritize security efforts and resource allocation. Later on, organizations can integrate robust security measures by leveraging two key frameworks: OWASP SAMM for application security management and NIST CSF 2.0 for overall security cybersecurity management. This blog compares both frameworks, highlighting their distinct focuses on overall cybersecurity and application security, and their complementary roles in managing organizational security risks.
Security Frameworks and Implementation Tools for HIPAA Adherence
The use of OWASP SAMM to assess the current maturity levels across SAMM’s functional areas helps develop a roadmap for improvement based on identified gaps while adopting NIST CSF 2.0 for overall security assists in aligning organizational practices with the framework’s core functions. Moreover, HIPAA also requires the integration of physical security measures aligned with ISO 27001.
For a more extensive dive into the different layers of frameworks, check out this blog.
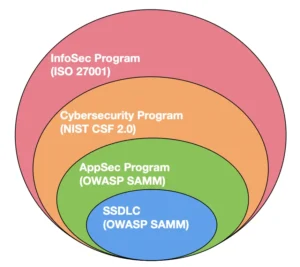
Healthcare organizations can utilize various tools and frameworks to facilitate HIPAA implementation. To manage the implementation of these frameworks and physical security measures, organizations can utilize SAMMY, a free tool that facilitates the integration of SAMM, NIST CSF 2.0, and ISO 27001-aligned practices. This tool is particularly useful for HIPAA implementation, as it helps in assessing, auditing, and improving security posture, ensuring adherance with various regulatory standards. By employing these frameworks and tools in tandem, companies can create a comprehensive security program that not only meets HIPAA requirements but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices, ensuring the protection of sensitive health information across all aspects of their operations.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Training and Awareness
HIPAA training for all staff members is a crucial yet tedious part of the acquiescence. Online platforms like Compliancy Group or the HIPAA E-tool offer courses covering HIPAA basics, privacy rules, security measures and role-specific responsibilities. By leveraging these tools, healthcare organizations can transform HIPAA training from a burdensome task into an opportunity for continuous improvement. Training should occur annually, with additional sessions for new hires or when significant changes occur in HIPAA regulations.
Incident Response
To address potential data breaches, organizations must create incident response plans. These plans should outline detection, reporting, and response procedures. Designate responsible personnel, such as a team leader or IT security specialist. Establish clear internal and external communication channels for swift information flow. Provide a step-by-step guide for containment and mitigation. This includes isolating affected systems, preserving evidence, and preventing further unauthorized access.
Risk Assessment
As HIPAA requires a risk assessment that evaluates potential impacts on individual privacy, threat modeling methodologies like LINDUNN are highly relevant. LINDDUN, which stands for Linking, Identifying, Non-repudiation, Detecting, Data Disclosure, Unawareness, and Non-compliance, offers a systematic approach to identifying and mitigating privacy threats early in the development lifecycle. Moreover, its focus on privacy threats within software systems contributes to its excellence in threat modeling. There are various software solutions available, like Log360 and SAMMY, that support the comprehensive auditing, monitoring and HIPAA compliance efforts.
Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance
To maintain continuous HIPAA implementation, healthcare organizations should:
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate measures.
- Provide ongoing security awareness training to all staff members.
- Implement robust administrative, physical, and technical safeguards, including encryption and access controls.
- Develop and maintain comprehensive policies and procedures for handling PHI.
- Create and regularly update an incident response plan, detailing roles, responsibilities, and steps for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents.
- Perform periodic internal audits and monitoring to assess HIPAA adherance and identify areas for improvement.
- Implement strong authentication measures, including complex passwords and regular password changes.
- Maintain detailed records and documentation of all compliance efforts and security measures.
- Utilize secure communication channels for sharing sensitive patient information.
- Regularly review and update security measures to adapt to evolving threats and regulations.
Conclusion
Implementing HIPAA compliance effectively requires a strategic plan that addresses risk assessment and security management. Free tools like SAMMY offer an accessible entry point for healthcare organizations looking to implement robust HIPAA compliance programs. Moreover by integrating OWASP SAMM, NIST CSF 2.0, and ISO 27001-aligned practices through SAMMY, healthcare entities can develop a holistic approach to compliance management, ensuring they meet HIPAA requirements while building authority and credibility in their security practices.